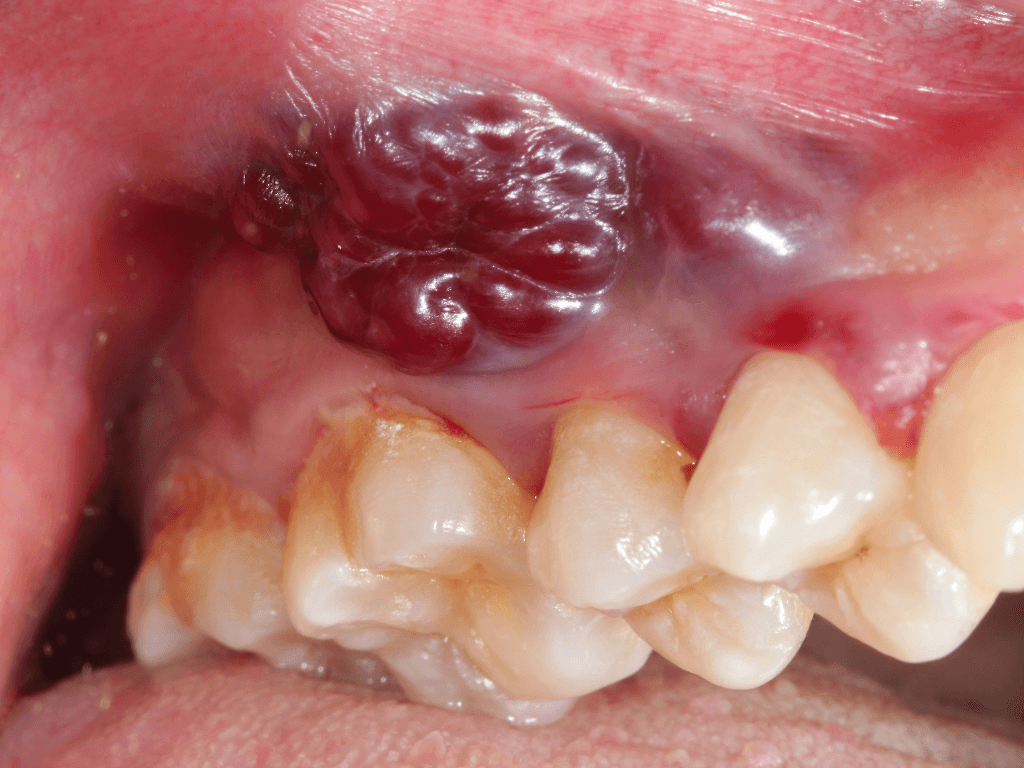
Oral cancer
Oral cancer is a malignant (cancerous) growth that develops in the tissues of the mouth or oral cavity. It can affect the lips, tongue, gums, cheeks, floor of the mouth, or roof of the mouth.
Causes / Risk Factors:
-
Tobacco use – Smoking cigarettes, cigars, or chewing tobacco
-
Alcohol consumption – Especially when combined with tobacco use
-
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection
-
Chronic irritation – From sharp teeth or ill-fitting dentures
-
Poor oral hygiene
-
Exposure to sunlight – For lip cancer
-
Nutritional deficiency – Especially vitamin A deficiency
Signs and Symptoms:
-
A non-healing ulcer or sore in the mouth (lasting more than 2 weeks)
-
Lump or thickening in the cheek or tongue
-
White or red patches (leukoplakia or erythroplakia) in the mouth
-
Pain or difficulty in chewing, swallowing, or speaking
-
Bleeding from the mouth
-
Loose teeth without obvious cause
-
Swelling of the jaw or neck lymph nodes
Diagnosis:
-
Clinical examination of the oral cavity
-
Biopsy (to confirm cancer cells)
-
Imaging tests – X-ray, CT scan, MRI for extent of spread
Treatment:
-
Surgery – To remove the tumor
-
Radiation therapy
-
Chemotherapy
-
Reconstructive surgery (if large area removed)
Prevention:
-
Avoid tobacco and alcohol
-
Maintain good oral hygiene
-
Eat a healthy, balanced diet
-
Protect lips from excessive sunlight
-
Regular dental check-ups for early detection

